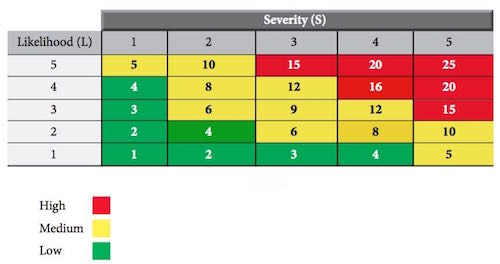
Risk can be presented in variety of ways to communicate the results of analysis to make decision on risk control. For risk analysis that uses likelihood and severity in qualitative method, presenting result in a risk matrix is a very effective way of communicating the distribution of the risk throughout a plant and area in a workplace.
L x S = Relative Risk
L = Likelihood
S = Severity
An example of risk matrix (Table C) is shown below:
Table C : Risk Matrix
To use this matrix, first find the severity column that best describes the outcome of risk. Then follow the likelihood row to find the description that best suits the likelihood that the severity will occur. The risk level is given in the box where the row and column meet.
The relative risk value can be used to prioritize necessary actions to effectively manage work place hazards. Table D determines priority based on the following ranges:
Table D : Relative Risk Value
Hazards assessed, as “High Risk” must have immediate actions, to resolve risk to life safety and or the environment. Individuals responsible for required action, including follow up must be clearly identified. A further detail risk assessment method may require such as quantitative risk assessment as means of determine suitable controls measures.