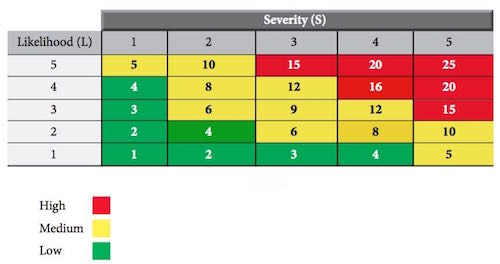
Occupational skin disease is a skin diseasecaused by exposure to hazardous agents or materialsfound in the workplace.
Occupational Contact Dermatitis
Thecharacteristics are skin becomes red, itchy, wateryand puffy after exposure or contact with theagents in the workplace. Usually occurs inparts of the body that come into direct contact with the agent, butit can spread to other places. Harmful agents that often causeare coloring materials, rubber, formaldehyde, powder, pesticides,organic solvents, cement, chemicals, detergents, diesel, paraffin and diluents.
Cancer that occurs after long exposure to specific agentsin the workplace. The skin becomesred, scaly, swollenand cut. Harmful agents that often causeare radiation, soot, tar and mineral lubricants.
Occupational Acne
Acne grows after exposure to certain substances at work.Harmful agents that often cause are oil and grease.
Occupational Leukoderma (Vitiligo)
White colored skinafter exposure to certain substances at work. Usually occurs in the arms and upper arms. Hazardousagents often causethe material containing phenol and hydroquinone.
Occupational skin diseases can be diagnosed in several ways. Occupational skin disease usually improves during the holidays and got worse after returning to work. In addition, specifictests such as a skin patch test and skin biopsy testsare needed for confirmation. (Specimens from theaffected skin are taken for examination under a microscope).
Prevention
Occupational skin diseases can be prevented as follows:- Avoid touching hazardous materials identified cause skin diseases.
- Use good personal hygiene. Wash the affected part of the body of dangerous substances in the workplace immediately.
- Use protective creams while working in exposure to sunlight.
- Wear personal protective equipment to prevent direct contact to hazardous agents. For example, gloves, goggles, long sleeves, long pants and apron as appropriate.
- Seek medical advice IMMEDIATELY if you experience work-related skin diseases.
- Report IMMEDIATELY to the employer so that appropriate control measures can be taken to improve working conditions)
Treatment options depend on the type and severity of the disease, type of skin diseases and chronic disease. The most important step is to prevent the recurrence of occupational skin disease is to avoid exposure or touching dangerous agents concerned. Medical treatment can be given to cure symptoms of itching, rashes and so on. Surgery is needed to remove skin cancer.