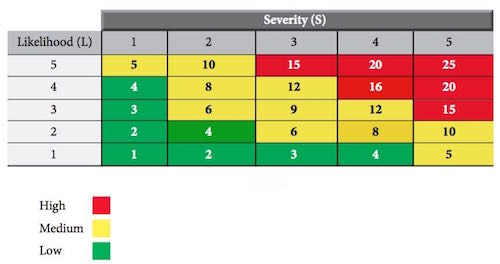
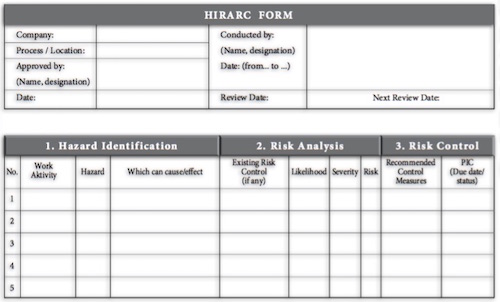
Thermal Stress is exposure to extreme temperatures either too cold or hot. Thermoregulation can be achieved by balancing the two main factors that determined the temperature of the body:
- Metabolic heat.
- The rate of heat loss.
Factors Influencing the ability to work:
1- Features of Employees:
- The reaction of the body against heat tolerance.
- Age.
- Fitness level.
- Acclimatisation.
2- Thermal environment:
- Relative humidity.
- Heat radiation (Globe Temperature).
- Wind speed.
3- Job requirements:
- The rate of work.
- Allocation of time to rest.
- Provision of personal protective clothing.
Working in cold environments
The following points need to be alerted when working in cold environments:
- Body temperature (Core Temperature) - not less than 25 degree Celcius.
- Adaptation to the cold.
- Perception of coolness.
- Skin temperature.
Health effects due to working in cold environments:
- Confusion.
- Frostbite.
- Hypothermia-drop in body temperature, and death.
Control measures on the health effects of working in cold environments:
- Set a safe work-rest cycle.
- Provide personal protective clothing.
Heat stress
Heat stress is an accumulation of heat in the body which exceed the ability of the body to remove it.
Risk Factors
1- Environment and type of work.
2- Features workers;
- Age.
- Gender.
- Obesity.
- Medicines.
- Diseases.
- Dietary factors.
Effects of Physiology
- The central nervous system.
- Muscle activity and work capacity.
- Control blood circulation.
- Perspiration mechanisms .
- Changes in the body's electrolyte balance.
- Changes in the endocrine system.
Health Effects
- Heat rash.
- Stiffness; Muscle spasm pain (especially muscle lower limbs).
- Fatigue; Fatigue, dizziness, fainting, blurred eyes, imbalance and excessive sweating.
- Heat stroke; Organ damage (brain, liver, kidney, muscle, homeopoitik system), hyperthermia (> 41 ° C), confusion, unconsciousness, seizures, dehydration, shock, and death.
Control Measures
1- Basic and safe operating procedures (SOP).
2- Engineering controls:
- Ventilation.
- Barriers / isolation.
3- Place for rest and drink water.
4- Personal protective equipment (clothing and equipment).
5- Training and education:
- The hazards of heat stress.
- Symptoms and signs.
- First aid procedures.
- Responsibilities of employees.
1- Environment and type of work.
2- Features workers;
- Age.
- Gender.
- Obesity.
- Medicines.
- Diseases.
- Dietary factors.
Effects of Physiology
- The central nervous system.
- Muscle activity and work capacity.
- Control blood circulation.
- Perspiration mechanisms .
- Changes in the body's electrolyte balance.
- Changes in the endocrine system.
Health Effects
- Heat rash.
- Stiffness; Muscle spasm pain (especially muscle lower limbs).
- Fatigue; Fatigue, dizziness, fainting, blurred eyes, imbalance and excessive sweating.
- Heat stroke; Organ damage (brain, liver, kidney, muscle, homeopoitik system), hyperthermia (> 41 ° C), confusion, unconsciousness, seizures, dehydration, shock, and death.
Control Measures
1- Basic and safe operating procedures (SOP).
2- Engineering controls:
- Ventilation.
- Barriers / isolation.
3- Place for rest and drink water.
4- Personal protective equipment (clothing and equipment).
5- Training and education:
- The hazards of heat stress.
- Symptoms and signs.
- First aid procedures.
- Responsibilities of employees.