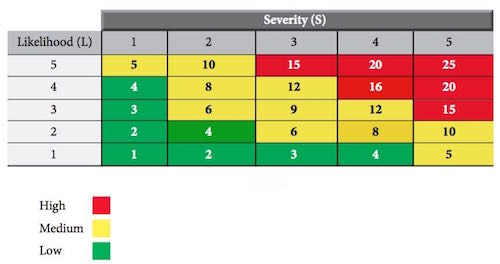
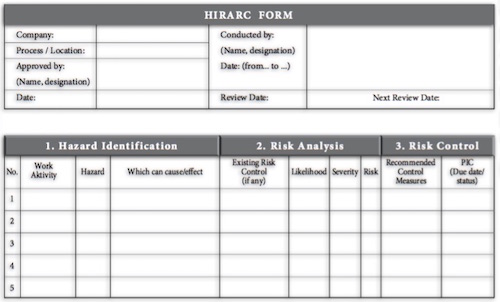
Compressed Gases - Most labs require compressed gas for various purposes. Compressed gases pose a unique danger. Some gas potentially hazardous chemical and mechanical. Gas may be flammable, explosive, is corrosive, toxic, inert or combination of various hazards. Flammable gas, a fire point lower than room temperature or diffuse rapidly is a potential for an explosion.
Because of the gas contained in the heavy cylinder and high pressure, the gas cylinder could potentially be a bomb or a rocket. Compressed gas cylinders must be clearly labelled so easily recognized by all employees. If the label on the cylinder is not clear and its contents are not known, the cylinder must be returned immediately to the supplier. Gas cylinders must be fastened vertically to a wall or lab table to avoid falling.
Each new cylinder acceptance must be examined to ensure no leakage, closed well and has a label that indicates the type of gas.
Cylinders containing flammable gases such as hydrogen or acetylene, should not be stored near sources of heat or sources of sparks. Use soap bubbles to test for leaks. All cylinders containing flammable gases should be stored in a well-ventilated area.
Oxygen gas cylinders either full or empty should be stored in areas away from flammable gases. Preferably the gas storage flammable gas and oxygen must be separated by a distance of at least 15 meters or separated by a fire barrier wall with "fire rating "of 0.5 hours.
Cryogenic Liquids
Cryogenic liquids can also be dangerous because of the extreme cold. The users must be trained before using cryogenic liquids.
-Fire or explosion
- Liquid nitrogen and oxygen cannot be used to cool a flammable mixture in the presence of air because oxygen can be condensed from the air and can cause an explosion.
- Adequate ventilation is essential to prevent the accumulation of flammable gases such as hydrogen, methane and acetylene.
-Pressure
High-pressure cylinders and other containers used to store liquefied gases shall be completed not more than 80% of its maximum capacity to avoid expansion due to temperature rise, which could lead to an explosion due to an increase in pressure.
-Tissue damage
Contact with cryogenic liquid can cause tissue damage similar to thermal effects. Prolonged contact may cause blood to clot. Special gloves and face shields should always be worn during handling cryogenic liquids.