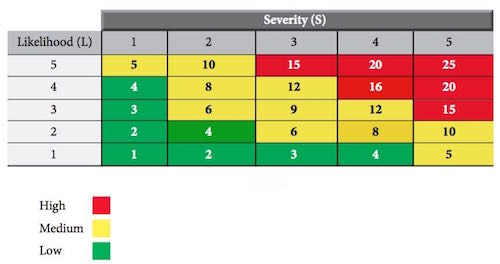
Auditory Effect
Exposure to prolonged and excessive noise level can cause noise induced hearing loss, which is permanent sensorineural condition that cannot be treated medically. It is initially characterized by declining sensitivity to high frequency sounds, usually at frequencies above 2000 Hz.
Later, the hearing loss proceeds for lower frequency sounds. If the exposure continuous for a long period of time it can result in permanent hearing loss. In this case the nerve hairs in the cochlea (inner ear) become damage and eventually die. Other symptom experienced is ringing sound in the ears (tinnitus).
On the other hand, short exposure to extremely loud noise (above 140 dB) such as in an explosion, can cause instant deafness due to mechanical rupture of eardrum or dislocation of the bones in the middle ear.
Non-Auditory Effect
Interference with communication and efficiency
- Noise also can be a safety hazard. Exposure to excessive noise level can cause difficulty in communication as well as fatigue. This can be a major problem in an emergency situation and will result in accident at workplace. It can also affect efficiency of workers either as a result of communication loss or by loss of concentration.
Psychosocial effect
- Noise can be a source of annoyance, irritation and increased stress.