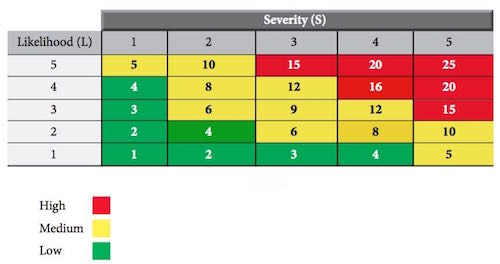
Ultraviolet, Infrared and Visible Radiation Hazards - Light is defined as electromagnetic radiation - a form of radient energy. There are many kinds of energy, including ultraviolet rays, infrared rays, radio waves and X-rays. We see only a minute part of the radient energy spectrum - the part which is called visible light.
Every type of radiation has its characteristic wavelength. UV, visible light and IR wavelengths are very small.-and are measured in nanometres (nm), i.e. billionths of a metre. Figure above shows the visible light region and the three regions from which the energy of ultraviolet, blue light and infrared can cause damage to the human eye.
How radiation affects the human eye?
How radiation affects the human eye?
The cornea is affected by ultraviolet radiation - primarily far-UV - as well as by mid-infrared. Damage can occur to the lens through the effects of near-UV and of infrared radiation which is primarily mid-IR. Other types of hazardous radiation are not absorbed by the cornea or lens, but focus directly on the retina This can be the case with the hazardous part of blue light (photo- chemical damage) as well as near-IR. The retina has a very limited capacity for healing; even low energy levels have been shown to cause retinal damage.
Additional factors should be considered in the case of outdoor work. In bright sunlight, glare attenuation may be an important requirement. A filter which relieves the eye from the effects of glare must also afford protection against UV and blue light as well as the considerable near-IR component of sunlight (about 46% of the sun's energy reaches the earth's surface).
Other complications can arise from exposure to IR. Indeed. infrared radiation can act in conjunction with blue light to lower photo-chemical damage thresholds. Similarly, since the cornea and lens are not cooled by their own blood-supply, IR can lower the UV damage thresholds of these organs. Protection against IR can also reduce eye-fatigue by reducing the heat load on the retina caused by the radiation. Figure below shows how radiation effects the eye.
Other complications can arise from exposure to IR. Indeed. infrared radiation can act in conjunction with blue light to lower photo-chemical damage thresholds. Similarly, since the cornea and lens are not cooled by their own blood-supply, IR can lower the UV damage thresholds of these organs. Protection against IR can also reduce eye-fatigue by reducing the heat load on the retina caused by the radiation. Figure below shows how radiation effects the eye.