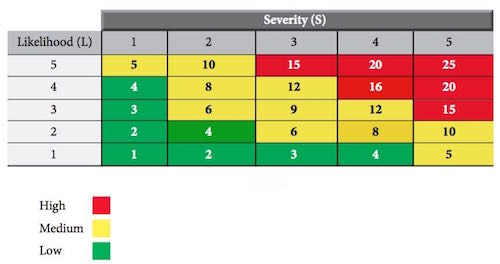
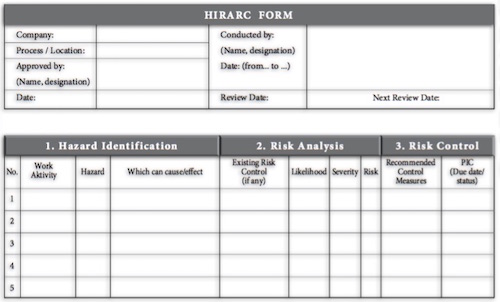
The purpose of hazard identification is to highlight the critical operations of tasks, that is, those tasks posing significant risks to the health and safety of employees as well as highlighting those hazards pertaining to certain equipment due to energy sources, working conditions or activities performed. Hazards can be divided into three main groups, health hazards, safety hazards, and environmental hazards.
Health Hazards
An occupational health hazard is any agent that can cause illness to an individual. A health hazard may produce serious and immediate (acute) affects, or may cause long-term (chronic) problems. All or part of the body may be affected. Someone with an occupational illness may not recognize the symptoms immediately. For example, noise-induced hearing loss is often difficult for the affected individual to detect until it is well advanced. Health hazards include chemicals (such as battery acid and solvents), biological hazards (such as bacteria, viruses, dusts and molds), physical agents (energy sources strong enough to harm the body, such as electric currents, heat, light, vibration, noise and radiation) and work design (ergonomic) hazards.
Safety Hazards
A safety hazard is any force strong enough to cause injury, or damage to property. An injury caused by a safety hazard is usually obvious. For example, a worker may be badly cut. Safety hazards cause harm when workplace controls are not adequate.
Some examples of safety hazards include, but are not limited to -
- slipping/tripping hazards (such as wires run across floors);
- fire hazards (from flammable materials);
- moving parts of machinery, tools and equipment (such as pinch and nip points);
- work at height (such as work done on scaffolds);
- ejection of material (such as from molding);
- pressure systems (such as steam boilers and pipes);
- vehicles (such as forklifts and trucks);
- lifting and other manual handling operations; and
- working alone.
Environmental Hazards
An environmental hazard is a release to the environment that may cause harm or deleterious effects. An environmental release may not be obvious. For example, a worker who drains a glycol system and releases the liquid to a storm sewer may not be aware, of the effect on the environment. Environmental hazards cause harm when controls and work procedures are not followed.