- Safe work procedures - Workers can be required to use standardized safety practices. The employer is expected to ensure that workers follow these practices. Work procedures must be periodically reviewed with workers and updated.
- Supervision and training – Initial training on safe work procedures and refresher training should be offered. Appropriate supervision to assist workers in identifying possible hazards and evaluating work procedures.
- Job rotations and other procedures can reduce the time that workers are exposed to a hazard. For example, workers can be rotated through jobs requiring repetitive tendon and muscle movements to prevent cumulative trauma injuries. Noisy processes can be scheduled when no one is in the workplace.
- Housekeeping, repair and maintenance programs - Housekeeping includes cleaning, waste disposal and spill cleanup. Tools, equipment and machinery are less likely to cause injury if they are kept clean and well maintained.
- Hygiene - Hygiene practices can reduce the risk of toxic materials being absorbed by workers or carried home to their families. Street clothing should be kept in separate lockers to avoid being contaminated by work clothing. Eating areas must be segregated from toxic hazards. Eating should be forbidden in toxic work areas. Where applicable, workers should be required to shower and change clothes at the end of the shift.
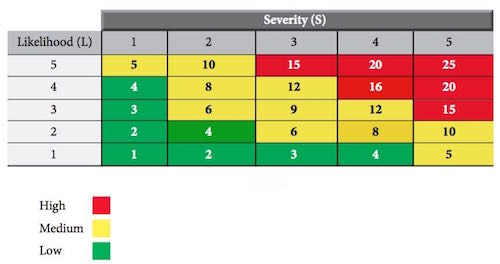
Types of Control : Administrative controls
abah
9:08 AM
Tags
Reactions
You may like these posts
ARCHIVE
Copyright © 2016 safetyrisks All Right Reserved
Popular Posts

HIRARC : Documenting Process
11:45 AM

Process of HIRARC
2:28 PM
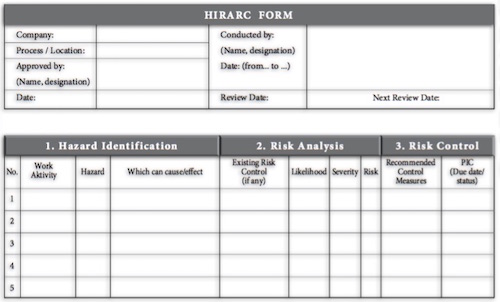
Documenting HIRARC
5:50 AM

Mechanical Hazards
4:20 AM
Categories
- PPE
- noise
- workplace safety
- electrical safety
- construction safety
- Occupational Safety and Health
- road safety
- OSHA
- chemical safety
- fire safety
- lab safety
- office safety
- safety engineering
- biological safety
- child safety
- computer safety
- environment
- escalator safety
- food safety
- forklift safety
- highway safety
- home safety
- hygiene
- industrial safety
- kitchen safety
- mechanical safety
- patient safety
- scaffolding safety
Tags
- HIRARC
- safety topics
- construction
- noise
- hazards
- Industrial Hygiene
- LOTO
- job hazard analysis
- demolition
- electrical
- fire
- hot work
- confined space
- first aid
- fishing
- flammable
- hearing impairment
- radiation
- safety officer
- safety signage
- Eye Protection
- Hand and Power Tools
- OSHA Certification
- administrative controls
- assessment
- biological
- body protective equipment
- breathing apparatus
- building evacuation
- chemical exposure
- compressed gases
- crane
- drowning
- emergency
- escalator
- evacuation
- excavation
- explosive
- forklift
- ghs hazard symbols
- how to
- physical hazards
- rescue
- risk management
Created By eaadhar | Distributed By Blogger Themes